Peripheral Artery Disease
Understanding Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatments
What Is Peripheral Arterial Disease?
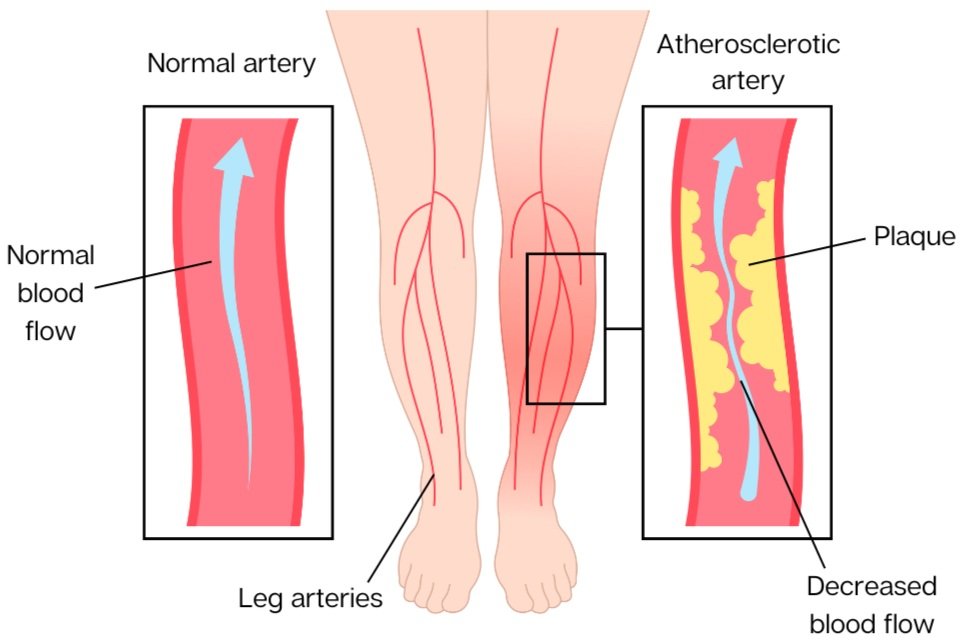
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a disease that occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the limbs become narrow or blocked, reducing blood flow and leading to a range of symptoms. This blockage that is developed in the arteries is a buildup of plaque. PAD is mostly seen in the legs, but can also appear in the arteries that supply blood from your heart to your head, arms, kidneys and stomach. Almost everyone who are diagnosed with PAD suffer from pain in their feet and an inability to walk as normal as they once did before developing the condition.
What are the Causes of PAD?
Identifying a single cause of PAD and the plaque buildup in the limbs is difficult at the moment. However, there are some risk factors that increase your chance of developing PAD which includes:
You are over the age of 50
Smoke or used to smoke
Have diabetes
Struggle with obesity
Have high blood pressure and cholesterol
Have a history of vascular disease, heart attack, or stroke
You are African American – twice as likely to get PAD
What are the Symptoms of PAD?
Many of the symptoms for PAD are ignored by both patients and physicians. Here are some of the things to look out for:
Claudication – fatigue or pain in leg muscles when walking that is only relieved during rest
Sores or wounds on toes, feet, or legs that heal slowly or not at all
Pain in legs or feet that disturbs sleep
A decreased temperature in one leg compared to the other
Changes in the skin on your legs or feet – color, hair loss, poor nail growth
Peripheral neuropathy – burning sensation in the feet which does not respond to medication
How is PAD Diagnosed?
In order to diagnose PAD, one must be able to recognize the symptoms. Most of the time, people with PAD symptoms often connect them with aging or another illness. By being cautious of the risk factors of PAD and its symptoms, people may be able to better convey their health issues to their doctors, and then receive a proper diagnosis. There are several tests doctors use to diagnose and confirm PAD, which includes:
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): A non-invasive test that compares the blood pressure in your ankle to the blood pressure in your arm. It shows how well the blood flow is in your limbs, however, it doesn’t identify which blood vessels are blocked or narrowed. The test also might be done before and after walking on a treadmill to determine the progression of PAD.
Pulse Volume Recording (PVR): It is a non-invasive test measures blood flow in your limbs. It uses ultrasound to evaluate circulation in your arteries and to locate the blockages within them.
Angiogram: A minimally invasive test that uses X-ray technology to detect blockage or narrowing in the arteries. This procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible tube into an artery in the leg and injecting a contrast agent that makes the arteries visible on the X-ray.
How is PAD Treated?
The main goals for treating PAD are to reduce your symptoms, improve quality of life and mobility, and to prevent other health complications that come with the disease, such as heart attack and stroke. There are three main approaches people can take in treating PAD: making lifestyle changes, taking medication to manage symptoms, and having a minimally invasive procedure. You can consult with your doctor to determine what the best treatment is for you.
Make Lifestyle Changes
In order to treat PAD, it requires you to make major changes to your everyday lifestyle. Some impactful change you can implement to help lower your risk of PAD includes:
Quit smoking
Lower your numbers (high blood pressure, cholesterol levels)
Follow a healthy diet plan
Get more physically active
Get yourself to a healthy weight
Medication for PAD
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage PAD. These may include:
Antiplatelet agents, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, to prevent blood clots
Cholesterol-lowering medications, such as statins, to reduce plaque buildup
Blood pressure medications to help control hypertension
Medications to manage blood sugar levels in patients with diabetes
Minimally Invasive Procedures for PAD
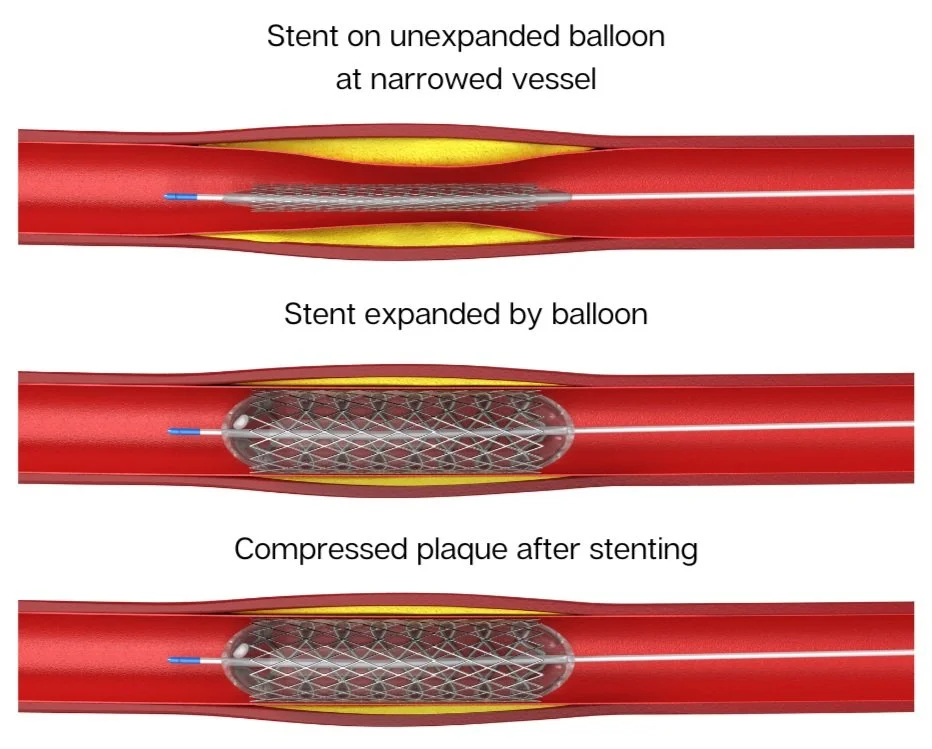
Angioplasty a minimally invasive procedure that is performed under local anesthesia. A balloon-tipped catheter is inserted into a blood vessel in your groin area, then using x-ray guidance, it is positioned to the artery that is being treated. The balloon is then inflated which presses the plaque against the artery wall, while at the same time expanding the artery and restoring its blood flow. After, the balloon is deflated and the catheter is removed from your body.
Angioplasty
Stents are usually placed together with the angioplasty procedure. The stent is made of a metal and mesh tube that expands to hold the artery open. After the balloon from the angioplasty is removed, the stent stays in place in order for blood to flow through that artery.
Stent Placement
An atherectomy involves the usage of a catheter and x-ray guidance like angioplasty and stent placement, but the main difference is that the catheter used for this procedure has a sharp blade that is used to remove plaque from your blocked blood vessel.
Atherectomy
Treating PAD at Indiana Vascular
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a prevalent and potentially dangerous condition that affects millions of people worldwide. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage the disease and reduce their risk of complications.
At Indiana Vascular, we offer a facility filled with state-of-the-art equipment and a staff of experienced doctors that specialize in treating PAD, as well as other conditions. We will work with you in creating a treatment plan tailored to your individualized needs, and will walk with you every step of the way to ensure a favorable outcome and swift recovery.
Do not allow PAD to negatively impact your quality of life. Schedule an appointment with us today to receive a consultation and gain insight into the condition, as well as discover how we can enhance your overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
While there is no cure for PAD, the condition can be managed effectively through lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, medical procedures or surgeries.
-
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced diet, not smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce the risk of developing PAD. Additionally, managing blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels can help prevent the disease.
-
If left untreated, PAD can lead to severe complications, including critical limb ischemia, gangrene, limb amputation, heart attack, and stroke. Early detection and proper management of PAD can help prevent these complications.
-
The frequency of doctor visits will depend on the severity of your condition and any other underlying health issues. It is essential to follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for checkups and monitoring of your PAD. Regular appointments can help ensure that your treatment plan remains effective and any changes in your condition are addressed promptly.